We had to plane a route for mountain biking using a map of the area that we were going to use, this was called Howden Reservoir.

We had to put crosses where we would want to stop for a rest and we had to describe what we would be able to see around us when we would stop .When we wa planning the route we used grid reference to found out were a place would be The trip around the lake was approximately 14km. the route we were taking was over different terrains, gradients and safetys. For some of the journey we were on roads so we look out for cars that were coming and make sure that we were all safe.
We had to measure the distance around the lake which was about 14km. We did this becuase each box on the map was 1km, so we measure the distanced by using the boxes, we could have an approximate distance set out of each leg of our journey were like 2 - 3 km each. We guessed that it would take an hour and half to get all way round, but when we actually took part in the ride it took us 1 hour and 45 minutes, this was becuase some of us was slower then others so people who were at the frount had to wait for the people who were at the back, but everyone helpped each other out. Some of the journey was hard and at one point i had to get of and push the bike up a hill but it was fun to take part in beucase we all did it together and i would do it again. When we stopped at one of the points we all needed a drink becuase it was really warm so some of us drunk out of the river, so next time i will make sure i take some water.
Aiming off and hand rail features
Aiming off and using hand rail features and features to relocate all involve using the landmarks of a location to help you along a route. Aiming off and using hand rail features both involve using land marks to help find and locate where you need to go and to help you stay en route, using features to relocate is something you do when you need to go back and find your position.

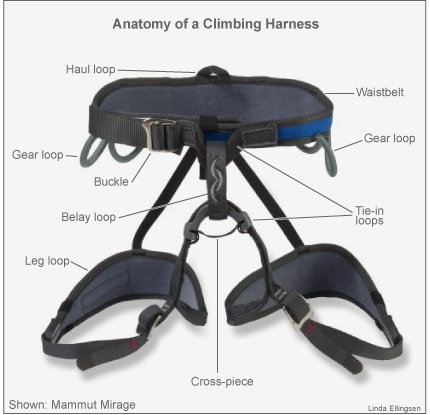
 The belayer should keep the rope locked off in the belay device whenever the climber is not moving. As the climber moves on the climb, the belayer must make sure that the climber has the right amount of rope by paying out or pulling in excess rope. If the climber falls, then they will free-fall the distance of the slack or unprotected rope before friction applied by the belayer will start to slow their descent. Too much slack on the rope will increase the distance which may be fallen, but too little slack on the rope may prevent the climber from being able to continue to move up the rock. It is extremely important for the belayer to concentrate on the climber's situation, as their role is crucial for the climber's safety.
The belayer should keep the rope locked off in the belay device whenever the climber is not moving. As the climber moves on the climb, the belayer must make sure that the climber has the right amount of rope by paying out or pulling in excess rope. If the climber falls, then they will free-fall the distance of the slack or unprotected rope before friction applied by the belayer will start to slow their descent. Too much slack on the rope will increase the distance which may be fallen, but too little slack on the rope may prevent the climber from being able to continue to move up the rock. It is extremely important for the belayer to concentrate on the climber's situation, as their role is crucial for the climber's safety.